mirror of
https://github.com/oven-sh/bun
synced 2026-02-10 02:48:50 +00:00
## Summary Updates documentation for all major features and changes introduced in Bun v1.3.2 blog post. ## Changes ### Package Manager - ✅ Document `configVersion` system for controlling default linker behavior - ✅ Clarify that "existing projects (made pre-v1.3.2)" use hoisted installs for backward compatibility - ✅ Add smart postinstall script optimization with environment variable flags - ✅ Document improved Git dependency resolution with HTTP tarball optimization - ✅ Add `bun list` alias for `bun pm ls` ### Testing - ✅ Document new `onTestFinished` lifecycle hook with simple example - ✅ Add to lifecycle hooks table in test documentation ### Runtime & Performance - ✅ Add CPU profiling with `--cpu-prof` flag documentation - ✅ Place after memory usage section for better flow ### WebSockets - ✅ Add `subscriptions` getter to existing pub/sub example - ✅ Add TypeScript reference for the subscriptions property ## Documentation Improvements All documentation now consistently: - Uses "made pre-v1.3.2" to clarify existing project behavior - Simplifies default linker explanations with clear references to `/docs/pm/isolated-installs` - Uses `/docs/pm/isolated-installs` for all internal references - Avoids confusing technical details in favor of user-friendly summaries ## Files Modified - `docs/guides/install/add-git.mdx` - Added GitHub tarball optimization note - `docs/pm/cli/install.mdx` - Added installation strategies and smart postinstall docs - `docs/pm/cli/pm.mdx` - Added bun list alias - `docs/pm/isolated-installs.mdx` - Updated default behavior section with configVersion table - `docs/project/benchmarking.mdx` - Added CPU profiling section - `docs/runtime/bunfig.mdx` - Clarified install.linker defaults - `docs/runtime/http/websockets.mdx` - Added subscriptions to example and TypeScript interface - `docs/test/lifecycle.mdx` - Added onTestFinished hook documentation ## Diff ````diff diff --git a/docs/guides/install/add-git.mdx b/docs/guides/install/add-git.mdx index 70950e1a63..7f8f3c8d81 100644 --- a/docs/guides/install/add-git.mdx +++ b/docs/guides/install/add-git.mdx @@ -33,6 +33,8 @@ bun add git@github.com:lodash/lodash.git bun add github:colinhacks/zod ``` +**Note:** GitHub dependencies download via HTTP tarball when possible for faster installation. + --- See [Docs > Package manager](https://bun.com/docs/cli/install) for complete documentation of Bun's package manager. diff --git a/docs/pm/cli/install.mdx b/docs/pm/cli/install.mdx index 7affb62646..dde268b7e5 100644 --- a/docs/pm/cli/install.mdx +++ b/docs/pm/cli/install.mdx @@ -88,6 +88,13 @@ Lifecycle scripts will run in parallel during installation. To adjust the maximu bun install --concurrent-scripts 5 ``` +Bun automatically optimizes postinstall scripts for popular packages (like `esbuild`, `sharp`, etc.) by determining which scripts need to run. To disable these optimizations: + +```bash terminal icon="terminal" +BUN_FEATURE_FLAG_DISABLE_NATIVE_DEPENDENCY_LINKER=1 bun install +BUN_FEATURE_FLAG_DISABLE_IGNORE_SCRIPTS=1 bun install +``` + --- ## Workspaces @@ -231,7 +238,7 @@ Bun supports installing dependencies from Git, GitHub, and local or remotely-hos Bun supports two package installation strategies that determine how dependencies are organized in `node_modules`: -### Hoisted installs (default for single projects) +### Hoisted installs The traditional npm/Yarn approach that flattens dependencies into a shared `node_modules` directory: @@ -249,7 +256,15 @@ bun install --linker isolated Isolated installs create a central package store in `node_modules/.bun/` with symlinks in the top-level `node_modules`. This ensures packages can only access their declared dependencies. -For complete documentation on isolated installs, refer to [Package manager > Isolated installs](/pm/isolated-installs). +### Default strategy + +The default linker strategy depends on whether you're starting fresh or have an existing project: + +- **New workspaces/monorepos**: `isolated` (prevents phantom dependencies) +- **New single-package projects**: `hoisted` (traditional npm behavior) +- **Existing projects (made pre-v1.3.2)**: `hoisted` (preserves backward compatibility) + +The default is controlled by a `configVersion` field in your lockfile. For a detailed explanation, see [Package manager > Isolated installs](/docs/pm/isolated-installs). --- @@ -319,8 +334,7 @@ dryRun = false concurrentScripts = 16 # (cpu count or GOMAXPROCS) x2 # installation strategy: "hoisted" or "isolated" -# default: "hoisted" (for single-project projects) -# default: "isolated" (for monorepo projects) +# default varies by project type - see /docs/pm/isolated-installs linker = "hoisted" diff --git a/docs/pm/cli/pm.mdx b/docs/pm/cli/pm.mdx index fc297753d3..9c8faa7da1 100644 --- a/docs/pm/cli/pm.mdx +++ b/docs/pm/cli/pm.mdx @@ -115,6 +115,8 @@ To print a list of installed dependencies in the current project and their resol ```bash terminal icon="terminal" bun pm ls +# or +bun list ``` ```txt @@ -130,6 +132,8 @@ To print all installed dependencies, including nth-order dependencies. ```bash terminal icon="terminal" bun pm ls --all +# or +bun list --all ``` ```txt diff --git a/docs/pm/isolated-installs.mdx b/docs/pm/isolated-installs.mdx index 73c6748b15..17afe02fe1 100644 --- a/docs/pm/isolated-installs.mdx +++ b/docs/pm/isolated-installs.mdx @@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ description: "Strict dependency isolation similar to pnpm's approach" Bun provides an alternative package installation strategy called **isolated installs** that creates strict dependency isolation similar to pnpm's approach. This mode prevents phantom dependencies and ensures reproducible, deterministic builds. -This is the default installation strategy for monorepo projects. +This is the default installation strategy for **new** workspace/monorepo projects (with `configVersion = 1` in the lockfile). Existing projects continue using hoisted installs unless explicitly configured. ## What are isolated installs? @@ -43,8 +43,23 @@ linker = "isolated" ### Default behavior -- For monorepo projects, Bun uses the **isolated** installation strategy by default. -- For single-project projects, Bun uses the **hoisted** installation strategy by default. +The default linker strategy depends on your project's lockfile `configVersion`: + +| `configVersion` | Using workspaces? | Default Linker | +| --------------- | ----------------- | -------------- | +| `1` | ✅ | `isolated` | +| `1` | ❌ | `hoisted` | +| `0` | ✅ | `hoisted` | +| `0` | ❌ | `hoisted` | + +**New projects**: Default to `configVersion = 1`. In workspaces, v1 uses the isolated linker by default; otherwise it uses hoisted linking. + +**Existing Bun projects (made pre-v1.3.2)**: If your existing lockfile doesn't have a version yet, Bun sets `configVersion = 0` when you run `bun install`, preserving the previous hoisted linker default. + +**Migrations from other package managers**: + +- From pnpm: `configVersion = 1` (using isolated installs in workspaces) +- From npm or yarn: `configVersion = 0` (using hoisted installs) You can override the default behavior by explicitly specifying the `--linker` flag or setting it in your configuration file. diff --git a/docs/project/benchmarking.mdx b/docs/project/benchmarking.mdx index 1263a06729..2ab8bcafc8 100644 --- a/docs/project/benchmarking.mdx +++ b/docs/project/benchmarking.mdx @@ -216,3 +216,26 @@ numa nodes: 1 elapsed: 0.068 s process: user: 0.061 s, system: 0.014 s, faults: 0, rss: 57.4 MiB, commit: 64.0 MiB ``` + +## CPU profiling + +Profile JavaScript execution to identify performance bottlenecks with the `--cpu-prof` flag. + +```sh terminal icon="terminal" +bun --cpu-prof script.js +``` + +This generates a `.cpuprofile` file you can open in Chrome DevTools (Performance tab → Load profile) or VS Code's CPU profiler. + +### Options + +```sh terminal icon="terminal" +bun --cpu-prof --cpu-prof-name my-profile.cpuprofile script.js +bun --cpu-prof --cpu-prof-dir ./profiles script.js +``` + +| Flag | Description | +| ---------------------------- | -------------------- | +| `--cpu-prof` | Enable profiling | +| `--cpu-prof-name <filename>` | Set output filename | +| `--cpu-prof-dir <dir>` | Set output directory | diff --git a/docs/runtime/bunfig.mdx b/docs/runtime/bunfig.mdx index 91005c1607..5b7fe49823 100644 --- a/docs/runtime/bunfig.mdx +++ b/docs/runtime/bunfig.mdx @@ -497,9 +497,9 @@ print = "yarn" ### `install.linker` -Configure the default linker strategy. Default `"hoisted"` for single-project projects, `"isolated"` for monorepo projects. +Configure the linker strategy for installing dependencies. Defaults to `"isolated"` for new workspaces, `"hoisted"` for new single-package projects and existing projects (made pre-v1.3.2). -For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Isolated installs](/pm/isolated-installs). +For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Isolated installs](/docs/pm/isolated-installs). ```toml title="bunfig.toml" icon="settings" [install] diff --git a/docs/runtime/http/websockets.mdx b/docs/runtime/http/websockets.mdx index b33f37c29f..174043200d 100644 --- a/docs/runtime/http/websockets.mdx +++ b/docs/runtime/http/websockets.mdx @@ -212,6 +212,9 @@ const server = Bun.serve({ // this is a group chat // so the server re-broadcasts incoming message to everyone server.publish("the-group-chat", `${ws.data.username}: ${message}`); + + // inspect current subscriptions + console.log(ws.subscriptions); // ["the-group-chat"] }, close(ws) { const msg = `${ws.data.username} has left the chat`; @@ -393,6 +396,7 @@ interface ServerWebSocket { readonly data: any; readonly readyState: number; readonly remoteAddress: string; + readonly subscriptions: string[]; send(message: string | ArrayBuffer | Uint8Array, compress?: boolean): number; close(code?: number, reason?: string): void; subscribe(topic: string): void; diff --git a/docs/test/lifecycle.mdx b/docs/test/lifecycle.mdx index 6427175df6..3837f0e948 100644 --- a/docs/test/lifecycle.mdx +++ b/docs/test/lifecycle.mdx @@ -6,11 +6,12 @@ description: "Learn how to use beforeAll, beforeEach, afterEach, and afterAll li The test runner supports the following lifecycle hooks. This is useful for loading test fixtures, mocking data, and configuring the test environment. | Hook | Description | -| ------------ | --------------------------- | +| ---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- | | `beforeAll` | Runs once before all tests. | | `beforeEach` | Runs before each test. | | `afterEach` | Runs after each test. | | `afterAll` | Runs once after all tests. | +| `onTestFinished` | Runs after a single test finishes (after all `afterEach`). | ## Per-Test Setup and Teardown @@ -90,6 +91,23 @@ describe("test group", () => { }); ``` +### `onTestFinished` + +Use `onTestFinished` to run a callback after a single test completes. It runs after all `afterEach` hooks. + +```ts title="test.ts" icon="/icons/typescript.svg" +import { test, onTestFinished } from "bun:test"; + +test("cleanup after test", () => { + onTestFinished(() => { + // runs after all afterEach hooks + console.log("test finished"); + }); +}); +``` + +Not supported in concurrent tests; use `test.serial` instead. + ## Global Setup and Teardown To scope the hooks to an entire multi-file test run, define the hooks in a separate file. ```` 🤖 Generated with [Claude Code](https://claude.com/claude-code) --------- Co-authored-by: Claude Bot <claude-bot@bun.sh> Co-authored-by: Claude <noreply@anthropic.com> Co-authored-by: autofix-ci[bot] <114827586+autofix-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Michael H <git@riskymh.dev> Co-authored-by: Lydia Hallie <lydiajuliettehallie@gmail.com>
488 lines
14 KiB
Plaintext
488 lines
14 KiB
Plaintext
---
|
|
title: "bun install"
|
|
description: "Install packages with Bun's fast package manager"
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
import Install from "/snippets/cli/install.mdx";
|
|
|
|
## Basic Usage
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install react
|
|
bun install react@19.1.1 # specific version
|
|
bun install react@latest # specific tag
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `bun` CLI contains a Node.js-compatible package manager designed to be a dramatically faster replacement for `npm`, `yarn`, and `pnpm`. It's a standalone tool that will work in pre-existing Node.js projects; if your project has a `package.json`, `bun install` can help you speed up your workflow.
|
|
|
|
<Note>
|
|
|
|
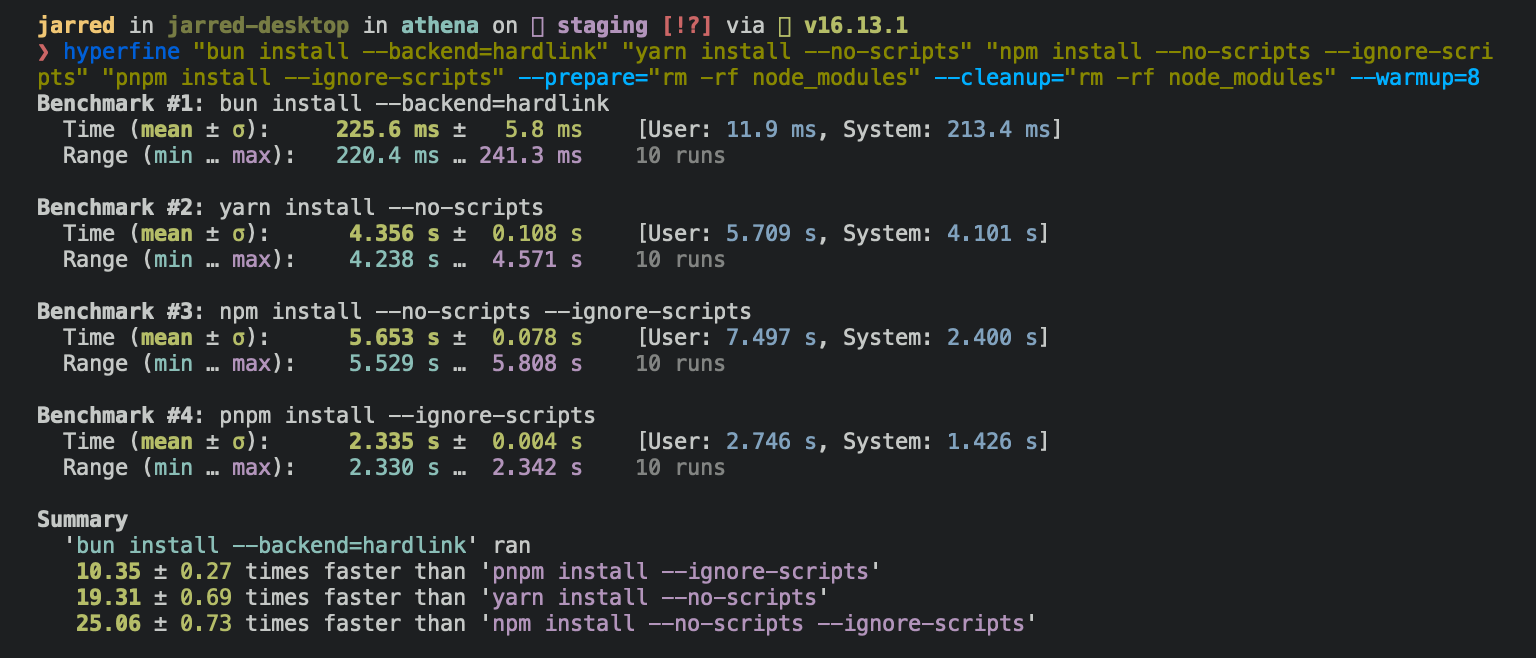
**⚡️ 25x faster** — Switch from `npm install` to `bun install` in any Node.js project to make your installations up to 25x faster.
|
|
|
|
<Frame>
|
|
|
|
</Frame>
|
|
|
|
</Note>
|
|
|
|
<Accordion title="For Linux users">
|
|
The recommended minimum Linux Kernel version is 5.6. If you're on Linux kernel 5.1 - 5.5, `bun install` will work, but HTTP requests will be slow due to a lack of support for io_uring's `connect()` operation.
|
|
|
|
If you're using Ubuntu 20.04, here's how to install a [newer kernel](https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Kernel/LTSEnablementStack):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# If this returns a version >= 5.6, you don't need to do anything
|
|
uname -r
|
|
|
|
# Install the official Ubuntu hardware enablement kernel
|
|
sudo apt install --install-recommends linux-generic-hwe-20.04
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
</Accordion>
|
|
|
|
To install all dependencies of a project:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Running `bun install` will:
|
|
|
|
- **Install** all `dependencies`, `devDependencies`, and `optionalDependencies`. Bun will install `peerDependencies` by default.
|
|
- **Run** your project's `{pre|post}install` and `{pre|post}prepare` scripts at the appropriate time. For security reasons Bun _does not execute_ lifecycle scripts of installed dependencies.
|
|
- **Write** a `bun.lock` lockfile to the project root.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Logging
|
|
|
|
To modify logging verbosity:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --verbose # debug logging
|
|
bun install --silent # no logging
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Lifecycle scripts
|
|
|
|
Unlike other npm clients, Bun does not execute arbitrary lifecycle scripts like `postinstall` for installed dependencies. Executing arbitrary scripts represents a potential security risk.
|
|
|
|
To tell Bun to allow lifecycle scripts for a particular package, add the package to `trustedDependencies` in your package.json.
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"version": "1.0.0",
|
|
"trustedDependencies": ["my-trusted-package"] // [!code ++]
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Then re-install the package. Bun will read this field and run lifecycle scripts for `my-trusted-package`.
|
|
|
|
Lifecycle scripts will run in parallel during installation. To adjust the maximum number of concurrent scripts, use the `--concurrent-scripts` flag. The default is two times the reported cpu count or GOMAXPROCS.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --concurrent-scripts 5
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Bun automatically optimizes postinstall scripts for popular packages (like `esbuild`, `sharp`, etc.) by determining which scripts need to run. To disable these optimizations:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
BUN_FEATURE_FLAG_DISABLE_NATIVE_DEPENDENCY_LINKER=1 bun install
|
|
BUN_FEATURE_FLAG_DISABLE_IGNORE_SCRIPTS=1 bun install
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Workspaces
|
|
|
|
Bun supports `"workspaces"` in package.json. For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Workspaces](/pm/workspaces).
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"version": "1.0.0",
|
|
"workspaces": ["packages/*"], // [!code ++]
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"preact": "^10.5.13"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Installing dependencies for specific packages
|
|
|
|
In a monorepo, you can install the dependencies for a subset of packages using the `--filter` flag.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Install dependencies for all workspaces except `pkg-c`
|
|
bun install --filter '!pkg-c'
|
|
|
|
# Install dependencies for only `pkg-a` in `./packages/pkg-a`
|
|
bun install --filter './packages/pkg-a'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For more information on filtering with `bun install`, refer to [Package Manager > Filtering](/pm/filter#bun-install-and-bun-outdated)
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Overrides and resolutions
|
|
|
|
Bun supports npm's `"overrides"` and Yarn's `"resolutions"` in `package.json`. These are mechanisms for specifying a version range for _metadependencies_—the dependencies of your dependencies. Refer to [Package manager > Overrides and resolutions](/pm/overrides) for complete documentation.
|
|
|
|
```json package.json file="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"foo": "^2.0.0"
|
|
},
|
|
"overrides": {
|
|
// [!code ++]
|
|
"bar": "~4.4.0" // [!code ++]
|
|
} // [!code ++]
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Global packages
|
|
|
|
To install a package globally, use the `-g`/`--global` flag. Typically this is used for installing command-line tools.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --global cowsay # or `bun install -g cowsay`
|
|
cowsay "Bun!"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```txt
|
|
______
|
|
< Bun! >
|
|
------
|
|
\ ^__^
|
|
\ (oo)\_______
|
|
(__)\ )\/\
|
|
||----w |
|
|
|| ||
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Production mode
|
|
|
|
To install in production mode (i.e. without `devDependencies` or `optionalDependencies`):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --production
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For reproducible installs, use `--frozen-lockfile`. This will install the exact versions of each package specified in the lockfile. If your `package.json` disagrees with `bun.lock`, Bun will exit with an error. The lockfile will not be updated.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --frozen-lockfile
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For more information on Bun's lockfile `bun.lock`, refer to [Package manager > Lockfile](/pm/lockfile).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Omitting dependencies
|
|
|
|
To omit dev, peer, or optional dependencies use the `--omit` flag.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Exclude "devDependencies" from the installation. This will apply to the
|
|
# root package and workspaces if they exist. Transitive dependencies will
|
|
# not have "devDependencies".
|
|
bun install --omit dev
|
|
|
|
# Install only dependencies from "dependencies"
|
|
bun install --omit=dev --omit=peer --omit=optional
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Dry run
|
|
|
|
To perform a dry run (i.e. don't actually install anything):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --dry-run
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Non-npm dependencies
|
|
|
|
Bun supports installing dependencies from Git, GitHub, and local or remotely-hosted tarballs. For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Git, GitHub, and tarball dependencies](/pm/cli/add).
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"dayjs": "git+https://github.com/iamkun/dayjs.git",
|
|
"lodash": "git+ssh://github.com/lodash/lodash.git#4.17.21",
|
|
"moment": "git@github.com:moment/moment.git",
|
|
"zod": "github:colinhacks/zod",
|
|
"react": "https://registry.npmjs.org/react/-/react-18.2.0.tgz",
|
|
"bun-types": "npm:@types/bun"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Installation strategies
|
|
|
|
Bun supports two package installation strategies that determine how dependencies are organized in `node_modules`:
|
|
|
|
### Hoisted installs
|
|
|
|
The traditional npm/Yarn approach that flattens dependencies into a shared `node_modules` directory:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --linker hoisted
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Isolated installs
|
|
|
|
A pnpm-like approach that creates strict dependency isolation to prevent phantom dependencies:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --linker isolated
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Isolated installs create a central package store in `node_modules/.bun/` with symlinks in the top-level `node_modules`. This ensures packages can only access their declared dependencies.
|
|
|
|
### Default strategy
|
|
|
|
The default linker strategy depends on whether you're starting fresh or have an existing project:
|
|
|
|
- **New workspaces/monorepos**: `isolated` (prevents phantom dependencies)
|
|
- **New single-package projects**: `hoisted` (traditional npm behavior)
|
|
- **Existing projects (made pre-v1.3.2)**: `hoisted` (preserves backward compatibility)
|
|
|
|
The default is controlled by a `configVersion` field in your lockfile. For a detailed explanation, see [Package manager > Isolated installs](/pm/isolated-installs).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Minimum release age
|
|
|
|
To protect against supply chain attacks where malicious packages are quickly published, you can configure a minimum age requirement for npm packages. Package versions published more recently than the specified threshold (in seconds) will be filtered out during installation.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Only install package versions published at least 3 days ago
|
|
bun add @types/bun --minimum-release-age 259200 # seconds
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also configure this in `bunfig.toml`:
|
|
|
|
```toml bunfig.toml icon="settings"
|
|
[install]
|
|
# Only install package versions published at least 3 days ago
|
|
minimumReleaseAge = 259200 # seconds
|
|
|
|
# Exclude trusted packages from the age gate
|
|
minimumReleaseAgeExcludes = ["@types/node", "typescript"]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
When the minimum age filter is active:
|
|
|
|
- Only affects new package resolution - existing packages in `bun.lock` remain unchanged
|
|
- All dependencies (direct and transitive) are filtered to meet the age requirement when being resolved
|
|
- When versions are blocked by the age gate, a stability check detects rapid bugfix patterns
|
|
- If multiple versions were published close together just outside your age gate, it extends the filter to skip those potentially unstable versions and selects an older, more mature version
|
|
- Searches up to 7 days after the age gate, however if still finding rapid releases it ignores stability check
|
|
- Exact version requests (like `package@1.1.1`) still respect the age gate but bypass the stability check
|
|
- Versions without a `time` field are treated as passing the age check (npm registry should always provide timestamps)
|
|
|
|
For more advanced security scanning, including integration with services & custom filtering, see [Package manager > Security Scanner API](/pm/security-scanner-api).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Configuration
|
|
|
|
The default behavior of `bun install` can be configured in `bunfig.toml`. The default values are shown below.
|
|
|
|
```toml bunfig.toml icon="settings"
|
|
[install]
|
|
|
|
# whether to install optionalDependencies
|
|
optional = true
|
|
|
|
# whether to install devDependencies
|
|
dev = true
|
|
|
|
# whether to install peerDependencies
|
|
peer = true
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--production` flag
|
|
production = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--save-text-lockfile` flag
|
|
saveTextLockfile = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--frozen-lockfile` flag
|
|
frozenLockfile = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--dry-run` flag
|
|
dryRun = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--concurrent-scripts` flag
|
|
concurrentScripts = 16 # (cpu count or GOMAXPROCS) x2
|
|
|
|
# installation strategy: "hoisted" or "isolated"
|
|
# default depends on lockfile configVersion and workspaces:
|
|
# - configVersion = 1: "isolated" if using workspaces, otherwise "hoisted"
|
|
# - configVersion = 0: "hoisted"
|
|
linker = "hoisted"
|
|
|
|
|
|
# minimum age config
|
|
minimumReleaseAge = 259200 # seconds
|
|
minimumReleaseAgeExcludes = ["@types/node", "typescript"]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## CI/CD
|
|
|
|
Use the official [`oven-sh/setup-bun`](https://github.com/oven-sh/setup-bun) action to install `bun` in a GitHub Actions pipeline:
|
|
|
|
```yaml .github/workflows/release.yml icon="file-code"
|
|
name: bun-types
|
|
jobs:
|
|
build:
|
|
name: build-app
|
|
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
steps:
|
|
- name: Checkout repo
|
|
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
|
- name: Install bun
|
|
uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v2
|
|
- name: Install dependencies
|
|
run: bun install
|
|
- name: Build app
|
|
run: bun run build
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For CI/CD environments that want to enforce reproducible builds, use `bun ci` to fail the build if the package.json is out of sync with the lockfile:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun ci
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This is equivalent to `bun install --frozen-lockfile`. It installs exact versions from `bun.lock` and fails if `package.json` doesn't match the lockfile. To use `bun ci` or `bun install --frozen-lockfile`, you must commit `bun.lock` to version control.
|
|
|
|
And instead of running `bun install`, run `bun ci`.
|
|
|
|
```yaml .github/workflows/release.yml icon="file-code"
|
|
name: bun-types
|
|
jobs:
|
|
build:
|
|
name: build-app
|
|
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
steps:
|
|
- name: Checkout repo
|
|
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
|
- name: Install bun
|
|
uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v2
|
|
- name: Install dependencies
|
|
run: bun ci
|
|
- name: Build app
|
|
run: bun run build
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## pnpm migration
|
|
|
|
Bun automatically migrates projects from pnpm to bun. When a `pnpm-lock.yaml` file is detected and no `bun.lock` file exists, Bun will automatically migrate the lockfile to `bun.lock` during installation. The original `pnpm-lock.yaml` file remains unmodified.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
**Note**: Migration only runs when `bun.lock` is absent. There is currently no opt-out flag for pnpm migration.
|
|
|
|
The migration process handles:
|
|
|
|
### Lockfile Migration
|
|
|
|
- Converts `pnpm-lock.yaml` to `bun.lock` format
|
|
- Preserves package versions and resolution information
|
|
- Maintains dependency relationships and peer dependencies
|
|
- Handles patched dependencies with integrity hashes
|
|
|
|
### Workspace Configuration
|
|
|
|
When a `pnpm-workspace.yaml` file exists, Bun migrates workspace settings to your root `package.json`:
|
|
|
|
```yaml pnpm-workspace.yaml icon="file-code"
|
|
packages:
|
|
- "apps/*"
|
|
- "packages/*"
|
|
|
|
catalog:
|
|
react: ^18.0.0
|
|
typescript: ^5.0.0
|
|
|
|
catalogs:
|
|
build:
|
|
webpack: ^5.0.0
|
|
babel: ^7.0.0
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The workspace packages list and catalogs are moved to the `workspaces` field in `package.json`:
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"workspaces": {
|
|
"packages": ["apps/*", "packages/*"],
|
|
"catalog": {
|
|
"react": "^18.0.0",
|
|
"typescript": "^5.0.0"
|
|
},
|
|
"catalogs": {
|
|
"build": {
|
|
"webpack": "^5.0.0",
|
|
"babel": "^7.0.0"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Catalog Dependencies
|
|
|
|
Dependencies using pnpm's `catalog:` protocol are preserved:
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"react": "catalog:",
|
|
"webpack": "catalog:build"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Configuration Migration
|
|
|
|
The following pnpm configuration is migrated from both `pnpm-lock.yaml` and `pnpm-workspace.yaml`:
|
|
|
|
- **Overrides**: Moved from `pnpm.overrides` to root-level `overrides` in `package.json`
|
|
- **Patched Dependencies**: Moved from `pnpm.patchedDependencies` to root-level `patchedDependencies` in `package.json`
|
|
- **Workspace Overrides**: Applied from `pnpm-workspace.yaml` to root `package.json`
|
|
|
|
### Requirements
|
|
|
|
- Requires pnpm lockfile version 7 or higher
|
|
- Workspace packages must have a `name` field in their `package.json`
|
|
- All catalog entries referenced by dependencies must exist in the catalogs definition
|
|
|
|
After migration, you can safely remove `pnpm-lock.yaml` and `pnpm-workspace.yaml` files.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
<Install />
|