14 KiB
The bun CLI contains an npm-compatible package manager designed to be a faster replacement for existing package management tools like npm, yarn, and pnpm. It's designed for Node.js compatibility; use it in any Bun or Node.js project.
{% callout %}
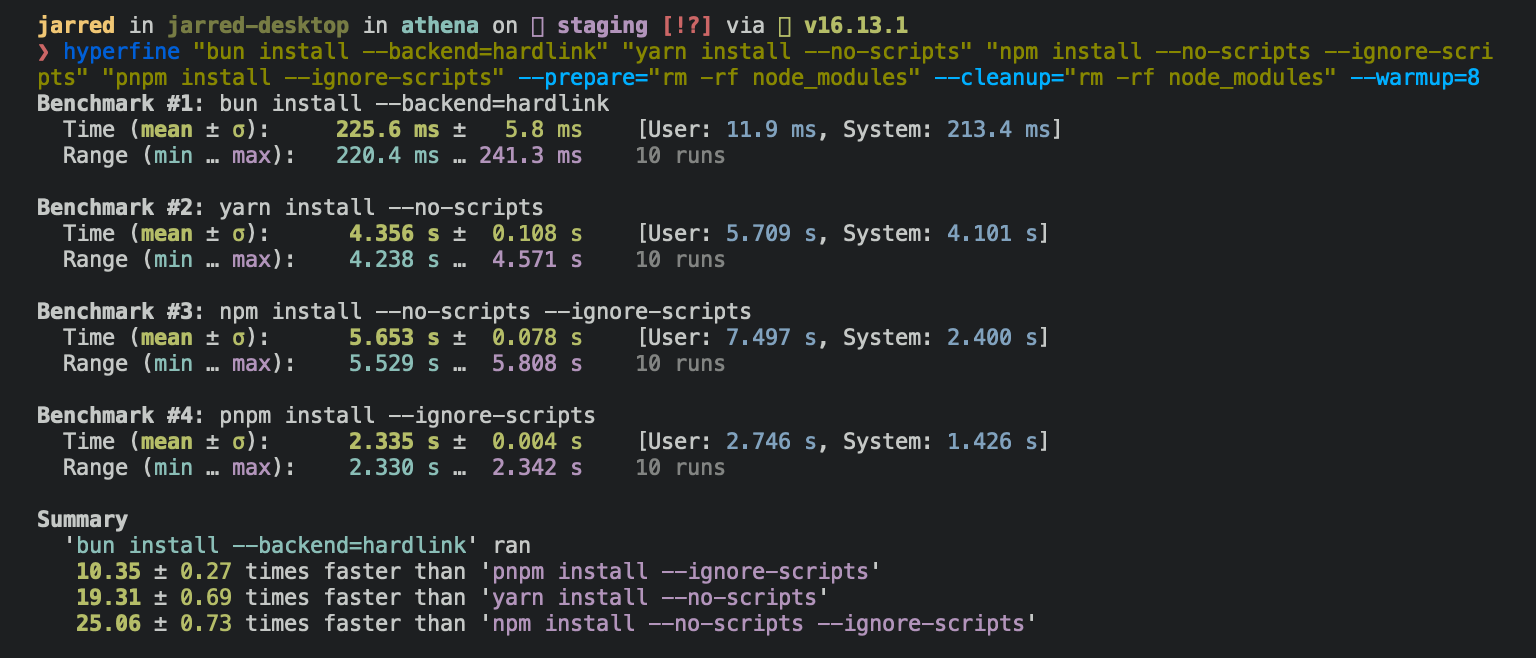
⚡️ 80x faster — Switch from npm install to bun install in any Node.js project to make your installations up to 80x faster.
{% image src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/709451/147004342-571b6123-17a9-49a2-8bfd-dcfc5204047e.png" height="200" /%}
{% /callout %}
{% details summary="For Linux users" %}
The minimum Linux Kernel version is 5.1. If you're on Linux kernel 5.1 - 5.5, bun install should still work, but HTTP requests will be slow due to a lack of support for io_uring's connect() operation.
If you're using Ubuntu 20.04, here's how to install a newer kernel:
# If this returns a version >= 5.6, you don't need to do anything
uname -r
# Install the official Ubuntu hardware enablement kernel
sudo apt install --install-recommends linux-generic-hwe-20.04
{% /details %}
Install dependencies
To install all dependencies of a project:
$ bun install
On Linux, bun install tends to install packages 20-100x faster than npm install. On macOS, it's more like 4-80x.
Running bun install will:
- Install all
dependencies,devDependencies, andoptionalDependencies. Bun does not installpeerDependenciesby default. - Run your project's
{pre|post}installscripts at the appropriate time. For security reasons Bun does not execute lifecycle scripts of installed dependencies. - Write a
bun.lockblockfile to the project root.
To install in production mode (i.e. without devDependencies):
$ bun install --production
To perform a dry run (i.e. don't actually install anything):
$ bun install --dry-run
To modify logging verbosity:
$ bun install --verbose # debug logging
$ bun install --silent # no logging
{% details summary="Configuring behavior" %}
The default behavior of bun install can be configured in bun.toml:
[install]
# whether to install optionalDependencies
optional = true
# whether to install devDependencies
dev = true
# whether to install peerDependencies
peer = false
# equivalent to `--production` flag
production = false
# equivalent to `--dry-run` flag
dryRun = false
{% /details %}
Add and remove packages
To add or remove a particular package:
$ bun add preact
$ bun remove preact
To specify a version, version range, or tag:
$ bun add zod@3.20.0
$ bun add zod@^3.0.0
$ bun add zod@latest
To add a package as a dev dependency ("devDependencies"):
$ bun add --development @types/react
$ bun add -d @types/react
To add a package as an optional dependency ("optionalDependencies"):
$ bun add --optional lodash
To install a package globally:
$ bun add --global cowsay # or `bun add -g cowsay`
$ cowsay "Bun!"
______
< Bun! >
------
\ ^__^
\ (oo)\_______
(__)\ )\/\
||----w |
|| ||
{% details summary="Configuring global installation behavior" %}
[install]
# where `bun install --global` installs packages
globalDir = "~/.bun/install/global"
# where globally-installed package bins are linked
globalBinDir = "~/.bun/bin"
{% /details %} To view a complete list of options for a given command:
$ bun add --help
Git dependencies
To add a dependency from a git repository:
$ bun install git@github.com:moment/moment.git
Bun supports a variety of protocols, including github, git, git+ssh, git+https, and many more.
{
"dependencies": {
"dayjs": "git+https://github.com/iamkun/dayjs.git",
"lodash": "git+ssh://github.com/lodash/lodash.git#4.17.21",
"moment": "git@github.com:moment/moment.git",
"zod": "github:colinhacks/zod"
}
}
Global cache
All packages downloaded from the registry are stored in a global cache at ~/.bun/install/cache. They are stored in subdirectories named like ${name}@${version}, so multiple versions of a package can be cached.
{% details summary="Configuring cache behavior" %}
[install.cache]
# the directory to use for the cache
dir = "~/.bun/install/cache"
# when true, don't load from the global cache.
# Bun may still write to node_modules/.cache
disable = false
# when true, always resolve the latest versions from the registry
disableManifest = false
{% /details %}
Minimizing re-downloads
Bun strives to avoid re-downloading packages mutiple times. When installing a package, if the cache already contains a version in the range specified by package.json, Bun will use the cached package instead of downloading it again.
{% details summary="Installation details" %}
If the semver version has pre-release suffix (1.0.0-beta.0) or a build suffix (1.0.0+20220101), it is replaced with a hash of that value instead, to reduce the chances of errors associated with long file paths.
When the node_modules folder exists, before installing, Bun checks that node_modules contains all expected packages with appropriate versions. If so bun install completes. Bun uses a custom JSON parser which stops parsing as soon as it finds "name" and "version".
If a package is missing or has a version incompatible with the package.json, Bun checks for a compatible module in the cache. If found, it is installed into node_modules. Otherwise, the package will be downloaded from the registry then installed.
{% /details %}
Fast copying
Once a package is downloaded into the cache, Bun still needs to copy those files into node_modules. Bun uses the fastest syscalls available to perform this task. On Linux, it uses hardlinks; on macOS, it uses clonefile.
Saving disk space
Since Bun uses hardlinks to "copy" a module into a project's node_modules directory on Linux, the contents of the package only exist in a single location on disk, greatly reducing the amount of disk space dedicated to node_modules.
This benefit does not extend to macOS, which uses clonefile for performance reasons.
{% details summary="Installation strategies" %}
This behavior is configurable with the --backend flag, which is respected by all of Bun's package management commands.
hardlink: Default on Linux.clonefileDefault on macOS.clonefile_each_dir: Similar toclonefile, except it clones each file individually per directory. It is only available on macOS and tends to perform slower thanclonefile.copyfile: The fallback used when any of the above fail. It is the slowest option. On macOS, it usesfcopyfile(); on Linux it usescopy_file_range().symlink: Currently used onlyfile:(and eventuallylink:) dependencies. To prevent infinite loops, it skips symlinking thenode_modulesfolder.
If you install with --backend=symlink, Node.js won't resolve node_modules of dependencies unless each dependency has its own node_modules folder or you pass --preserve-symlinks to node. See Node.js documentation on --preserve-symlinks.
$ bun install --backend symlink
$ node --preserve-symlinks ./foo.js
Bun's runtime does not currently expose an equivalent of --preserve-symlinks.
{% /details %}
Lockfile
Running bun install will create a binary lockfile called bun.lockb.
Why is it binary?
In a word: Performance. Bun’s lockfile saves & loads incredibly quickly, and saves a lot more data than what is typically inside lockfiles.
How do I inspect it?
Run bun install -y to generate a Yarn-compatible yarn.lock (v1) that can be inspected more easily.
Platform-specific dependencies?
Bun stores normalized cpu and os values from npm in the lockfile, along with the resolved packages. It skips downloading, extracting, and installing packages disabled for the current target at runtime. This means the lockfile won’t change between platforms/architectures even if the packages ultimately installed do change.
What does the lockfile store?
Packages, metadata for those packages, the hoisted install order, dependencies for each package, what packages those dependencies resolved to, an integrity hash (if available), what each package was resolved to, and which version (or equivalent).
Why is it fast?
It uses linear arrays for all data. Packages are referenced by an auto-incrementing integer ID or a hash of the package name. Strings longer than 8 characters are de-duplicated. Prior to saving on disk, the lockfile is garbage-collected & made deterministic by walking the package tree and cloning the packages in dependency order.
Can I opt out?
To install without creating a lockfile:
$ bun install --no-save
To install a Yarn lockfile in addition to bun.lockb.
{% codetabs %}
$ bun install --yarn
[install.lockfile]
# whether to save a non-Bun lockfile alongside bun.lockb
# only "yarn" is supported
print = "yarn"
{% /codetabs %}
{% details summary="Configuring lockfile" %}
[install.lockfile]
# path to read bun.lockb from
path = "bun.lockb"
# path to save bun.lockb to
savePath = "bun.lockb"
# whether to save the lockfile to disk
save = true
# whether to save a non-Bun lockfile alongside bun.lockb
# only "yarn" is supported
print = "yarn"
{% /details %}
Workspaces
Bun supports workspaces in package.json. Workspaces make it easy to develop complex software as a monorepo consisting of several independent packages.
To try it, specify a list of sub-packages in the workspaces field of your package.json; it's conventional to place these sub-packages in a directory called packages.
{
"name": "my-project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"workspaces": ["packages/*"]
}
{% callout %} Glob support — Bun v0.5.8 added support for simple globs for workspace names, with a "*/" at the end. Nothing too fancy. {% /callout %}
This has a couple major benefits.
- Code can be split into logical parts. If one package relies on another, you can simply add it as a dependency with
bun add. If packagebdepends ona,bun installwill symlink your localpackages/adirectory into thenode_modulesfolder ofb, instead of trying to download it from the npm registry. - Dependencies can be de-duplicated. If
aandbshare a common dependency, it will be hoisted to the rootnode_modulesdirectory. This reduces redundant disk usage and minimizes "dependency hell" issues associated with having multiple versions of a package installed simultaneously.
{% callout %}
⚡️ Speed — Installs are fast, even for big monorepos. Bun installs the Remix monorepo in about 500ms on Linux.
- 28x faster than
npm install - 12x faster than
yarn install(v1) - 8x faster than
pnpm install
{% image src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/709451/212829600-77df9544-7c9f-4d8d-a984-b2cd0fd2aa52.png" /%} {% /callout %}
Registries
The default registry is registry.npmjs.org. This can be globally configured in bunfig.toml:
[install]
# set default registry as a string
registry = "https://registry.npmjs.org"
# set a token
registry = { url = "https://registry.npmjs.org", token = "123456" }
# set a username/password
registry = "https://username:password@registry.npmjs.org"
To configure a private registry scoped to a particular organization:
[install.scopes]
# registry as string
"@myorg1" = "https://username:password@registry.myorg.com/"
# registry with username/password
# you can reference environment variables
"@myorg2" = { username = "myusername", password = "$NPM_PASS", url = "https://registry.myorg.com/" }
# registry with token
"@myorg3" = { token = "$npm_token", url = "https://registry.myorg.com/" }
Linking and unlinking
Use bun link in a local directory to register the current package as a "linkable" package.
$ cd /path/to/cool-pkg
$ cat package.json
{
"name": "cool-pkg",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
$ bun link
bun link v0.5.7 (7416672e)
Success! Registered "cool-pkg"
To use cool-pkg in a project, run:
bun link cool-pkg
Or add it in dependencies in your package.json file:
"cool-pkg": "link:cool-pkg"
This package can now be "linked" into other projects using bun link cool-pkg. This will create a symlink in the node_modules directory of the target project, pointing to the local directory.
$ cd /path/to/my-app
$ bun link cool-pkg
This will add cool-pkg to the dependencies field of your app's package.json with a special version specifier that tells Bun to load from the registered local directory instead of installing from npm.
{
"name": "my-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"dependencies": {
+ "cool-pkg": "link:cool-pkg"
}
}
Utilities
The bun pm command group provides a set of utilities for working with Bun's package manager.
To print the path to the bin directory for the local project:
$ bun pm bin
/path/to/current/project/node_modules/.bin
To get the path to the global bin directory:
$ bun pm bin
<$HOME>/.bun/bin
To print a list of packages installed in the current project and their resolved versions, excluding their dependencies. Use the --all flag to print the entire tree, including all nth-order dependencies.
$ bun pm ls
/path/to/project node_modules (5)
├── eslint@8.33.0
├── react@18.2.0
├── react-dom@18.2.0
├── typescript@4.8.4
└── zod@3.20.1
To print the path to Bun's global module cache:
$ bun pm cache
To clear Bun's global module cache:
$ bun pm cache rm