mirror of
https://github.com/oven-sh/bun
synced 2026-02-10 02:48:50 +00:00
472 lines
14 KiB
Plaintext
472 lines
14 KiB
Plaintext
---
|
|
title: "bun install"
|
|
description: "Install packages with Bun's fast package manager"
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
import Install from "/snippets/cli/install.mdx";
|
|
|
|
## Basic Usage
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install react
|
|
bun install react@19.1.1 # specific version
|
|
bun install react@latest # specific tag
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `bun` CLI contains a Node.js-compatible package manager designed to be a dramatically faster replacement for `npm`, `yarn`, and `pnpm`. It's a standalone tool that will work in pre-existing Node.js projects; if your project has a `package.json`, `bun install` can help you speed up your workflow.
|
|
|
|
<Note>
|
|
|
|
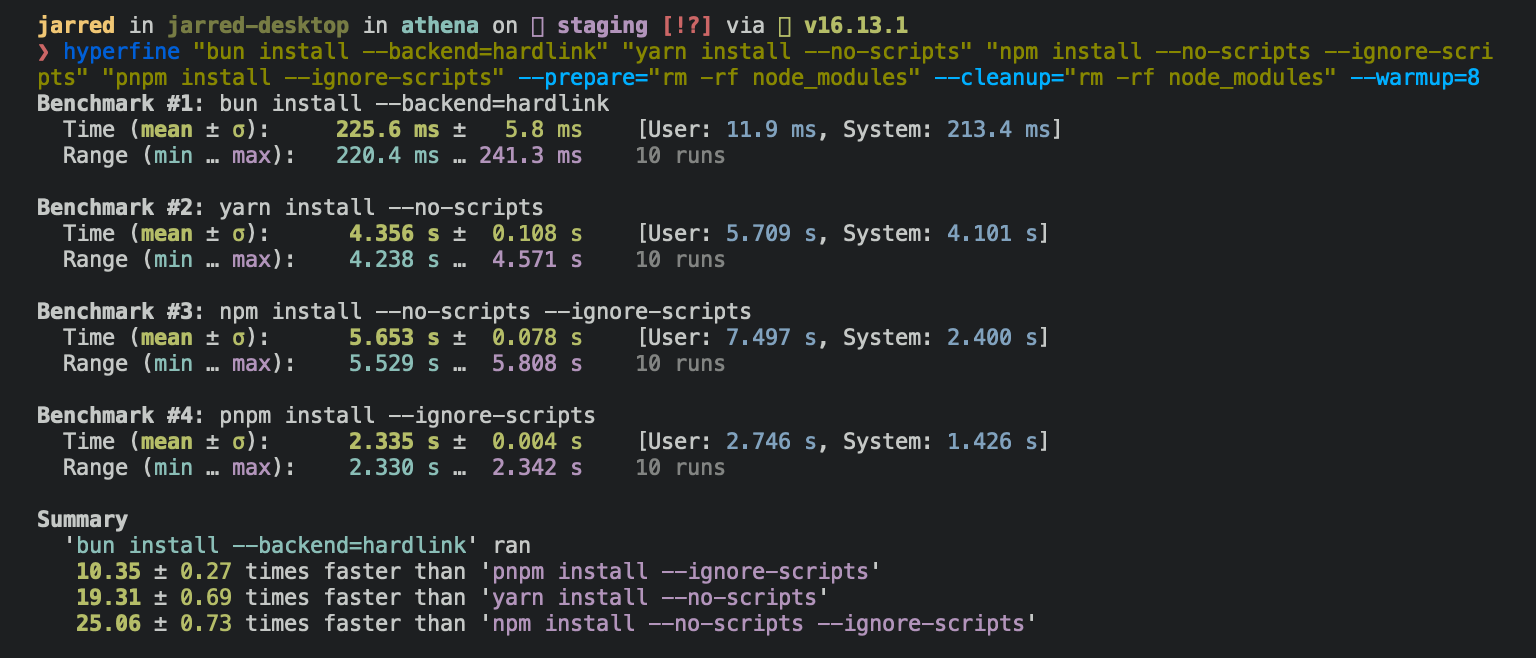
**⚡️ 25x faster** — Switch from `npm install` to `bun install` in any Node.js project to make your installations up to 25x faster.
|
|
|
|
<Frame>
|
|
|
|
</Frame>
|
|
|
|
</Note>
|
|
|
|
<Accordion title="For Linux users">
|
|
The recommended minimum Linux Kernel version is 5.6. If you're on Linux kernel 5.1 - 5.5, `bun install` will work, but HTTP requests will be slow due to a lack of support for io_uring's `connect()` operation.
|
|
|
|
If you're using Ubuntu 20.04, here's how to install a [newer kernel](https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Kernel/LTSEnablementStack):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# If this returns a version >= 5.6, you don't need to do anything
|
|
uname -r
|
|
|
|
# Install the official Ubuntu hardware enablement kernel
|
|
sudo apt install --install-recommends linux-generic-hwe-20.04
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
</Accordion>
|
|
|
|
To install all dependencies of a project:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Running `bun install` will:
|
|
|
|
- **Install** all `dependencies`, `devDependencies`, and `optionalDependencies`. Bun will install `peerDependencies` by default.
|
|
- **Run** your project's `{pre|post}install` and `{pre|post}prepare` scripts at the appropriate time. For security reasons Bun _does not execute_ lifecycle scripts of installed dependencies.
|
|
- **Write** a `bun.lock` lockfile to the project root.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Logging
|
|
|
|
To modify logging verbosity:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --verbose # debug logging
|
|
bun install --silent # no logging
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Lifecycle scripts
|
|
|
|
Unlike other npm clients, Bun does not execute arbitrary lifecycle scripts like `postinstall` for installed dependencies. Executing arbitrary scripts represents a potential security risk.
|
|
|
|
To tell Bun to allow lifecycle scripts for a particular package, add the package to `trustedDependencies` in your package.json.
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"version": "1.0.0",
|
|
"trustedDependencies": ["my-trusted-package"] // [!code ++]
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Then re-install the package. Bun will read this field and run lifecycle scripts for `my-trusted-package`.
|
|
|
|
Lifecycle scripts will run in parallel during installation. To adjust the maximum number of concurrent scripts, use the `--concurrent-scripts` flag. The default is two times the reported cpu count or GOMAXPROCS.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --concurrent-scripts 5
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Workspaces
|
|
|
|
Bun supports `"workspaces"` in package.json. For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Workspaces](/pm/workspaces).
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"version": "1.0.0",
|
|
"workspaces": ["packages/*"], // [!code ++]
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"preact": "^10.5.13"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Installing dependencies for specific packages
|
|
|
|
In a monorepo, you can install the dependencies for a subset of packages using the `--filter` flag.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Install dependencies for all workspaces except `pkg-c`
|
|
bun install --filter '!pkg-c'
|
|
|
|
# Install dependencies for only `pkg-a` in `./packages/pkg-a`
|
|
bun install --filter './packages/pkg-a'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For more information on filtering with `bun install`, refer to [Package Manager > Filtering](/pm/filter#bun-install-and-bun-outdated)
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Overrides and resolutions
|
|
|
|
Bun supports npm's `"overrides"` and Yarn's `"resolutions"` in `package.json`. These are mechanisms for specifying a version range for _metadependencies_—the dependencies of your dependencies. Refer to [Package manager > Overrides and resolutions](/pm/overrides) for complete documentation.
|
|
|
|
```json package.json file="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "my-app",
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"foo": "^2.0.0"
|
|
},
|
|
"overrides": {
|
|
// [!code ++]
|
|
"bar": "~4.4.0" // [!code ++]
|
|
} // [!code ++]
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Global packages
|
|
|
|
To install a package globally, use the `-g`/`--global` flag. Typically this is used for installing command-line tools.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --global cowsay # or `bun install -g cowsay`
|
|
cowsay "Bun!"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```txt
|
|
______
|
|
< Bun! >
|
|
------
|
|
\ ^__^
|
|
\ (oo)\_______
|
|
(__)\ )\/\
|
|
||----w |
|
|
|| ||
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Production mode
|
|
|
|
To install in production mode (i.e. without `devDependencies` or `optionalDependencies`):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --production
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For reproducible installs, use `--frozen-lockfile`. This will install the exact versions of each package specified in the lockfile. If your `package.json` disagrees with `bun.lock`, Bun will exit with an error. The lockfile will not be updated.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --frozen-lockfile
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For more information on Bun's lockfile `bun.lock`, refer to [Package manager > Lockfile](/pm/lockfile).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Omitting dependencies
|
|
|
|
To omit dev, peer, or optional dependencies use the `--omit` flag.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Exclude "devDependencies" from the installation. This will apply to the
|
|
# root package and workspaces if they exist. Transitive dependencies will
|
|
# not have "devDependencies".
|
|
bun install --omit dev
|
|
|
|
# Install only dependencies from "dependencies"
|
|
bun install --omit=dev --omit=peer --omit=optional
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Dry run
|
|
|
|
To perform a dry run (i.e. don't actually install anything):
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --dry-run
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Non-npm dependencies
|
|
|
|
Bun supports installing dependencies from Git, GitHub, and local or remotely-hosted tarballs. For complete documentation refer to [Package manager > Git, GitHub, and tarball dependencies](/pm/cli/add).
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"dayjs": "git+https://github.com/iamkun/dayjs.git",
|
|
"lodash": "git+ssh://github.com/lodash/lodash.git#4.17.21",
|
|
"moment": "git@github.com:moment/moment.git",
|
|
"zod": "github:colinhacks/zod",
|
|
"react": "https://registry.npmjs.org/react/-/react-18.2.0.tgz",
|
|
"bun-types": "npm:@types/bun"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Installation strategies
|
|
|
|
Bun supports two package installation strategies that determine how dependencies are organized in `node_modules`:
|
|
|
|
### Hoisted installs (default for single projects)
|
|
|
|
The traditional npm/Yarn approach that flattens dependencies into a shared `node_modules` directory:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --linker hoisted
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Isolated installs
|
|
|
|
A pnpm-like approach that creates strict dependency isolation to prevent phantom dependencies:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install --linker isolated
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Isolated installs create a central package store in `node_modules/.bun/` with symlinks in the top-level `node_modules`. This ensures packages can only access their declared dependencies.
|
|
|
|
For complete documentation on isolated installs, refer to [Package manager > Isolated installs](/pm/isolated-installs).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Minimum release age
|
|
|
|
To protect against supply chain attacks where malicious packages are quickly published, you can configure a minimum age requirement for npm packages. Package versions published more recently than the specified threshold (in seconds) will be filtered out during installation.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
# Only install package versions published at least 3 days ago
|
|
bun add @types/bun --minimum-release-age 259200 # seconds
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also configure this in `bunfig.toml`:
|
|
|
|
```toml bunfig.toml icon="settings"
|
|
[install]
|
|
# Only install package versions published at least 3 days ago
|
|
minimumReleaseAge = 259200 # seconds
|
|
|
|
# Exclude trusted packages from the age gate
|
|
minimumReleaseAgeExcludes = ["@types/node", "typescript"]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
When the minimum age filter is active:
|
|
|
|
- Only affects new package resolution - existing packages in `bun.lock` remain unchanged
|
|
- All dependencies (direct and transitive) are filtered to meet the age requirement when being resolved
|
|
- When versions are blocked by the age gate, a stability check detects rapid bugfix patterns
|
|
- If multiple versions were published close together just outside your age gate, it extends the filter to skip those potentially unstable versions and selects an older, more mature version
|
|
- Searches up to 7 days after the age gate, however if still finding rapid releases it ignores stability check
|
|
- Exact version requests (like `package@1.1.1`) still respect the age gate but bypass the stability check
|
|
- Versions without a `time` field are treated as passing the age check (npm registry should always provide timestamps)
|
|
|
|
For more advanced security scanning, including integration with services & custom filtering, see [Package manager > Security Scanner API](/pm/security-scanner-api).
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Configuration
|
|
|
|
The default behavior of `bun install` can be configured in `bunfig.toml`. The default values are shown below.
|
|
|
|
```toml bunfig.toml icon="settings"
|
|
[install]
|
|
|
|
# whether to install optionalDependencies
|
|
optional = true
|
|
|
|
# whether to install devDependencies
|
|
dev = true
|
|
|
|
# whether to install peerDependencies
|
|
peer = true
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--production` flag
|
|
production = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--save-text-lockfile` flag
|
|
saveTextLockfile = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--frozen-lockfile` flag
|
|
frozenLockfile = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--dry-run` flag
|
|
dryRun = false
|
|
|
|
# equivalent to `--concurrent-scripts` flag
|
|
concurrentScripts = 16 # (cpu count or GOMAXPROCS) x2
|
|
|
|
# installation strategy: "hoisted" or "isolated"
|
|
# default: "hoisted" (for single-project projects)
|
|
# default: "isolated" (for monorepo projects)
|
|
linker = "hoisted"
|
|
|
|
|
|
# minimum age config
|
|
minimumReleaseAge = 259200 # seconds
|
|
minimumReleaseAgeExcludes = ["@types/node", "typescript"]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## CI/CD
|
|
|
|
Use the official [`oven-sh/setup-bun`](https://github.com/oven-sh/setup-bun) action to install `bun` in a GitHub Actions pipeline:
|
|
|
|
```yaml .github/workflows/release.yml icon="file-code"
|
|
name: bun-types
|
|
jobs:
|
|
build:
|
|
name: build-app
|
|
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
steps:
|
|
- name: Checkout repo
|
|
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
|
- name: Install bun
|
|
uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v2
|
|
- name: Install dependencies
|
|
run: bun install
|
|
- name: Build app
|
|
run: bun run build
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For CI/CD environments that want to enforce reproducible builds, use `bun ci` to fail the build if the package.json is out of sync with the lockfile:
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun ci
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This is equivalent to `bun install --frozen-lockfile`. It installs exact versions from `bun.lock` and fails if `package.json` doesn't match the lockfile. To use `bun ci` or `bun install --frozen-lockfile`, you must commit `bun.lock` to version control.
|
|
|
|
And instead of running `bun install`, run `bun ci`.
|
|
|
|
```yaml .github/workflows/release.yml icon="file-code"
|
|
name: bun-types
|
|
jobs:
|
|
build:
|
|
name: build-app
|
|
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
steps:
|
|
- name: Checkout repo
|
|
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
|
- name: Install bun
|
|
uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v2
|
|
- name: Install dependencies
|
|
run: bun ci
|
|
- name: Build app
|
|
run: bun run build
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## pnpm migration
|
|
|
|
Bun automatically migrates projects from pnpm to bun. When a `pnpm-lock.yaml` file is detected and no `bun.lock` file exists, Bun will automatically migrate the lockfile to `bun.lock` during installation. The original `pnpm-lock.yaml` file remains unmodified.
|
|
|
|
```bash terminal icon="terminal"
|
|
bun install
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
**Note**: Migration only runs when `bun.lock` is absent. There is currently no opt-out flag for pnpm migration.
|
|
|
|
The migration process handles:
|
|
|
|
### Lockfile Migration
|
|
|
|
- Converts `pnpm-lock.yaml` to `bun.lock` format
|
|
- Preserves package versions and resolution information
|
|
- Maintains dependency relationships and peer dependencies
|
|
- Handles patched dependencies with integrity hashes
|
|
|
|
### Workspace Configuration
|
|
|
|
When a `pnpm-workspace.yaml` file exists, Bun migrates workspace settings to your root `package.json`:
|
|
|
|
```yaml pnpm-workspace.yaml icon="file-code"
|
|
packages:
|
|
- "apps/*"
|
|
- "packages/*"
|
|
|
|
catalog:
|
|
react: ^18.0.0
|
|
typescript: ^5.0.0
|
|
|
|
catalogs:
|
|
build:
|
|
webpack: ^5.0.0
|
|
babel: ^7.0.0
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The workspace packages list and catalogs are moved to the `workspaces` field in `package.json`:
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"workspaces": {
|
|
"packages": ["apps/*", "packages/*"],
|
|
"catalog": {
|
|
"react": "^18.0.0",
|
|
"typescript": "^5.0.0"
|
|
},
|
|
"catalogs": {
|
|
"build": {
|
|
"webpack": "^5.0.0",
|
|
"babel": "^7.0.0"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Catalog Dependencies
|
|
|
|
Dependencies using pnpm's `catalog:` protocol are preserved:
|
|
|
|
```json package.json icon="file-json"
|
|
{
|
|
"dependencies": {
|
|
"react": "catalog:",
|
|
"webpack": "catalog:build"
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Configuration Migration
|
|
|
|
The following pnpm configuration is migrated from both `pnpm-lock.yaml` and `pnpm-workspace.yaml`:
|
|
|
|
- **Overrides**: Moved from `pnpm.overrides` to root-level `overrides` in `package.json`
|
|
- **Patched Dependencies**: Moved from `pnpm.patchedDependencies` to root-level `patchedDependencies` in `package.json`
|
|
- **Workspace Overrides**: Applied from `pnpm-workspace.yaml` to root `package.json`
|
|
|
|
### Requirements
|
|
|
|
- Requires pnpm lockfile version 7 or higher
|
|
- Workspace packages must have a `name` field in their `package.json`
|
|
- All catalog entries referenced by dependencies must exist in the catalogs definition
|
|
|
|
After migration, you can safely remove `pnpm-lock.yaml` and `pnpm-workspace.yaml` files.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
<Install />
|